以前学习时一些零散的笔记, 新开一个系列.
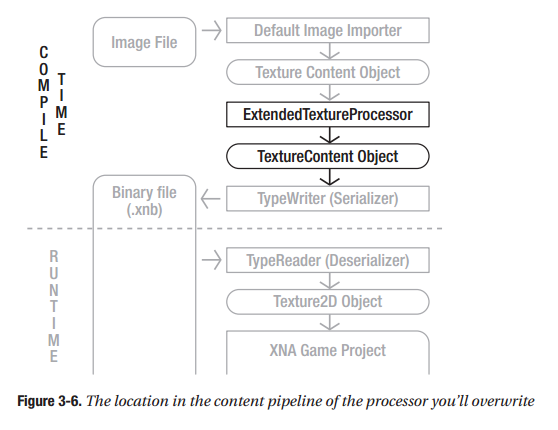
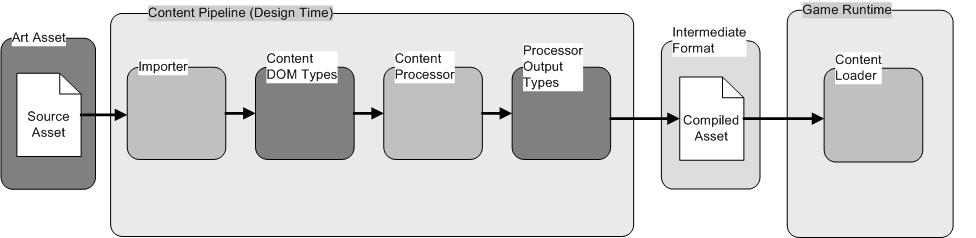
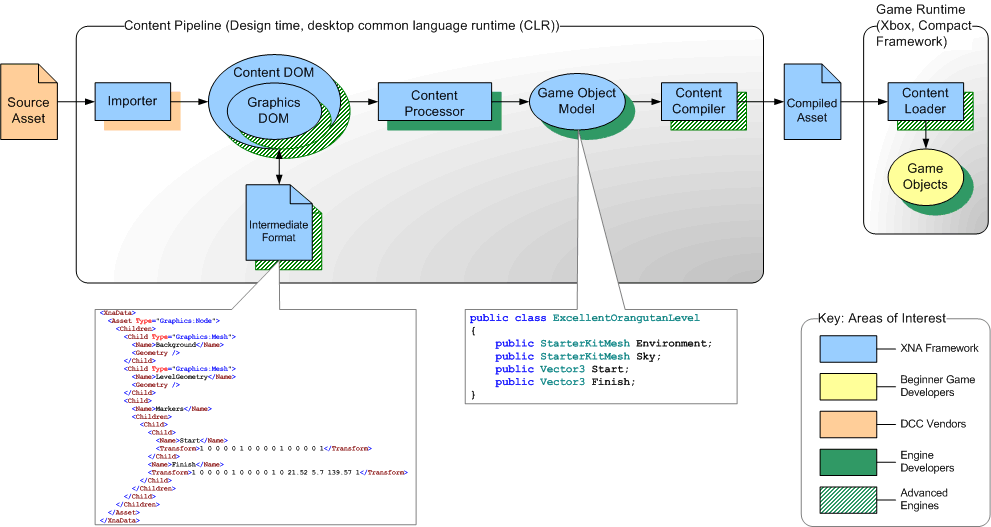
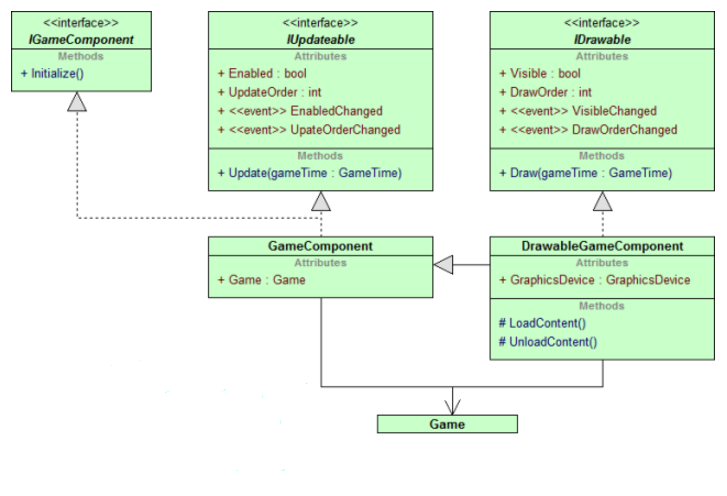
不管是side-scrolling(横版卷轴),还是tilemap,有一点是非常关键的,就是不同坐标系之间的变换。在三维中有一个视口变换。二维没有那么复杂,但原理差不多。Hero和地图上的tile(贴片),它们的位置是地图坐标,地图就是它们所在的世界,所以也可以说是世界坐标。在游戏逻辑中,Hero位置的改变,碰撞检测都是以地图坐标(世界坐标)进行的. 而在窗口屏幕中绘制Sprite和tile时,是以屏幕坐标为参照系的。因此在Draw方法中,必须将Hero和tile的地图坐标变换成屏幕坐标,从而在屏幕的适当位置显示出来。
1 | protected override void Update(GameTime gameTime) |
scroll表示游戏窗口与世界地图的相对位置, hero.Position表示hero的地图坐标, 如下图所示: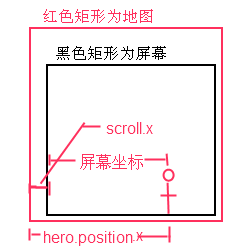
上面这段代码想要解决的一个设计场景是这样的: 以横版卷轴为例, 一开始屏幕位于地图最左侧, 此时Hero从屏幕左侧出生, 随后Hero往右移动. 当Hero未达到屏幕中间时, 屏幕是不会移动的. 当Hero达到屏幕中间, 此后屏幕和Hero一起往右移动, Hero始终占据屏幕的中心位置. 当屏幕达到地图最右侧时, 屏幕不再和Hero一起往右移动, Hero可以单独继续往右移动, 直到达到屏幕最右侧.
上面代码的关键是1
scroll += ((hero.Position - new Vector2(screenSize.X / 2f, screenSize.Y / 2f)) - scroll)
当未达到屏幕中间时, scroll会是一个负值, 如果是负值就会被重置为0, 屏幕停留在地图最左侧. 同理, 超出地图右侧.1
if (scroll.X < 0f) scroll.X = 0f;
那为什么要减去scroll呢?因为new Vector2(screenSize.X / 2f, screenSize.Y / 2f)是一个固定值,而hero.Position是一个不断变大的过程(往右移动), 假设前一帧移动后,hero.Position.x - screenSize.X = 10;这一帧移动后,hero.Position.x - screenSize.X = 20, 改变的是绝对值. 为了让不同性能的机子都能够流畅运行, scroll.x是以增量的形式增加的(scroll += ***), 即相对值. 因此需要减去原来的scroll得到一个增量,再将这个增量加回到scroll上.
这部分代码可以抽象出一个Camera2D类. scroll就是Camera2D的地图坐标, 屏幕大小就是Camera2D的ViewPort
1 | public class Camera2D |
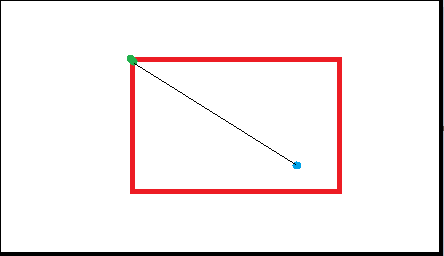
红色是视口,黑色是世界地图; 绿点是相机的Position(世界坐标); 蓝点是物体的Position(世界坐标)
官方有一个Camera2D的样例(http://xbox.create.msdn.com/en-US/education/catalog/sample/tiled_sprites), 支持rotation和zoom, 结构和上面介绍的有所不同
Although a game level might have tens of thousands of tiles in the game world, only those that are visible should be drawn. Otherwise, you see a severe performance hit for submitting more draw calls than are needed to render the scene.
To simplify interactions with the tiles in the game world, the sample provides a 2D Camera implementation. You will find a camera abstraction useful, particularly when rotating or zooming the world. This enables you to rapidly translate screen space to world space.
1 | namespace TiledSprites |
使用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68protected override void Update(GameTime gameTime)
{
//...
HandleGamePadInput((float)gameTime.ElapsedGameTime.TotalSeconds);
if (camera.IsChanged)
{
CameraChanged();
}
//...
}
public void HandleKeyboardInput(float elapsed)
{
//check for camera movement
float dX = ReadKeyboardAxis(currentKeyboardState, Keys.Left, Keys.Right) *
elapsed * MovementRate;
float dY = ReadKeyboardAxis(currentKeyboardState, Keys.Down, Keys.Up) *
elapsed * MovementRate;
camera.MoveRight(ref dX);
camera.MoveUp(ref dY);
//...
}
/// <summary>
/// This function is called when the camera's values have changed
/// and is used to update the properties of the tiles and animated sprite
/// </summary>
public void CameraChanged()
{
//set rotation
groundLayer.CameraRotation = detailLayer.CameraRotation =
cloudLayer.CameraRotation = rockLayer.CameraRotation =
animatedSprite.Rotation = camera.Rotation;
//set zoom
groundLayer.CameraZoom = detailLayer.CameraZoom =
rockLayer.CameraZoom = camera.Zoom;
animatedSprite.ScaleValue = animatedSpriteScale * camera.Zoom;
cloudLayer.CameraZoom = camera.Zoom + 1.0f;
//set position
groundLayer.CameraPosition = camera.Position;
detailLayer.CameraPosition = camera.Position;
rockLayer.CameraPosition = camera.Position;
//to acheive a paralax effect(视差效果), scale down cloud movement
cloudLayer.CameraPosition = camera.Position / 3.0f;
//...
}
/// <summary>
/// This is called when the game should draw itself.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="gameTime">Provides a snapshot of timing values.</param>
protected override void Draw(GameTime gameTime)
{
//...
groundLayer.Draw(spriteBatch);
detailLayer.Draw(spriteBatch);
rockLayer.Draw(spriteBatch);
animatedSprite.Draw(spriteBatch, Color.AntiqueWhite,
SpriteBlendMode.AlphaBlend);
//draw the clouds
cloudLayer.Draw(spriteBatch);
base.Draw(gameTime);
}